Get moving, instantly, with your go-to AI assistant
Input this prompt in your IDE to analyze your existing code base and generate SCIM implementation code accordingly.
*Compatible with Cursor, Windsurf, VS Code, and any AI-powered tools
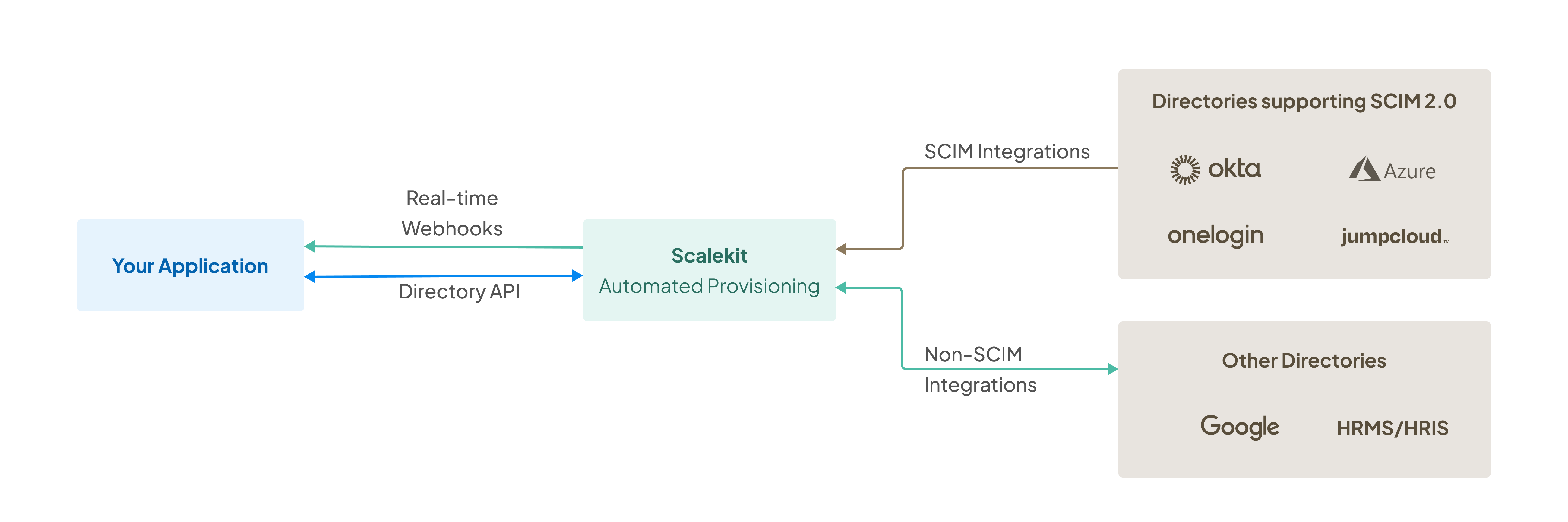
Automate user provisioning with SCIM. Directory API and webhooks for real-time user data sync
This guide shows you how to automate user provisioning with SCIM using Scalekit’s Directory API and webhooks. You’ll learn to sync user data in real-time, create webhook endpoints for instant updates, and build automated provisioning workflows that keep your application’s user data synchronized with your customers’ directory providers.
With SCIM Provisioning from Scalekit, you can:
Scalekit abstracts the complexities of various directory providers, giving you a single interface to automate user lifecycle management. This enables you to create accounts for new hires during onboarding, deactivate accounts when employees depart, and adjust access levels as employees change roles.
Input this prompt in your IDE to analyze your existing code base and generate SCIM implementation code accordingly.
*Compatible with Cursor, Windsurf, VS Code, and any AI-powered tools
Scalekit’s directory API allows you to fetch information about users, groups, and directories associated with an organization on-demand. This approach is ideal for scheduled synchronization tasks, bulk data imports, or when you need to ensure your application’s user data matches the latest directory provider state.
Let’s explore how to use the Directory API to retrieve user and group data programmatically.
Before you begin, ensure that your organization has a directory set up in Scalekit.
Scalekit offers language-specific SDKs for fast SSO integration. Use the installation instructions below for your technology stack:
npm install @scalekit-sdk/nodepip install scalekit-sdk-pythongo get -u github.com/scalekit-inc/scalekit-sdk-go/* Gradle users - add the following to your dependencies in build file */implementation "com.scalekit:scalekit-sdk-java:2.0.6"<!-- Maven users - add the following to your `pom.xml` --><dependency> <groupId>com.scalekit</groupId> <artifactId>scalekit-sdk-java</artifactId> <version>2.0.6</version></dependency>Navigate to Dashboard > Developers > Settings > API Credentials to obtain your credentials. Store your credentials securely in environment variables:
# Get these values from Dashboard > Developers > Settings > API CredentialsSCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL='https://b2b-app-dev.scalekit.com'SCALEKIT_CLIENT_ID='<CLIENT_ID_FROM_SCALEKIT_DASHBOARD>'SCALEKIT_CLIENT_SECRET='<SECRET_FROM_SCALEKIT_DASHBOARD>'Initialize the Scalekit client with your environment variables and make your first API call to list organizations.
# Security: Replace <ACCESS_TOKEN> with a valid access token from Scalekit# This token authorizes your API requests to access organization data
# Use case: Verify API connectivity and test authentication# Examples: Initial setup testing, debugging integration issues
curl -L "https://$SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL/api/v1/organizations?page_size=5" \-H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS_TOKEN>"4 collapsed lines
import { ScalekitClient } from '@scalekit-sdk/node';
// Initialize Scalekit client with environment variables// Security: Always use environment variables for sensitive credentialsconst scalekit = new ScalekitClient( process.env.SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL, process.env.SCALEKIT_CLIENT_ID, process.env.SCALEKIT_CLIENT_SECRET,);
try { // Use case: Retrieve organizations for bulk user provisioning workflows // Examples: Multi-tenant applications, enterprise customer onboarding const { organizations } = await scalekit.organization.listOrganization({ pageSize: 5, });
console.log(`Organization name: ${organizations[0].display_name}`); console.log(`Organization ID: ${organizations[0].id}`);} catch (error) { console.error('Failed to list organizations:', error); // Handle error appropriately for your application}4 collapsed lines
from scalekit import ScalekitClientimport os
# Initialize the SDK client with environment variables# Security: Use os.getenv() to securely access credentialsscalekit_client = ScalekitClient( env_url=os.getenv("SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL"), client_id=os.getenv("SCALEKIT_CLIENT_ID"), client_secret=os.getenv("SCALEKIT_CLIENT_SECRET"))
try: # Use case: Sync user data across multiple organizations # Examples: Scheduled provisioning tasks, HR system integration org_list = scalekit_client.organization.list_organizations(page_size='100')
if org_list: print(f'Organization details: {org_list[0]}') print(f'Organization ID: {org_list[0].id}')except Exception as error: print(f'Error listing organizations: {error}') # Implement appropriate error handling for your use case10 collapsed lines
package main
import ( "context" "fmt" "os"
"github.com/scalekit/scalekit-go")
// Initialize Scalekit client with environment variables// Security: Always load credentials from environment, not hardcodedscalekitClient := scalekit.NewScalekitClient( os.Getenv("SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL"), os.Getenv("SCALEKIT_CLIENT_ID"), os.Getenv("SCALEKIT_CLIENT_SECRET"),)
// Use case: Get specific organization for directory sync operations// Examples: Targeted user provisioning, organization-specific workflowsorganization, err := scalekitClient.Organization.GetOrganization( ctx, organizationId,)if err != nil { // Handle error appropriately for your application return fmt.Errorf("failed to get organization: %w", err)}8 collapsed lines
import com.scalekit.ScalekitClient;
// Initialize Scalekit client with environment variables// Security: Use System.getenv() to securely access credentialsScalekitClient scalekitClient = new ScalekitClient( System.getenv("SCALEKIT_ENVIRONMENT_URL"), System.getenv("SCALEKIT_CLIENT_ID"), System.getenv("SCALEKIT_CLIENT_SECRET"));
try { // Use case: List organizations for automated provisioning workflows // Examples: Enterprise customer setup, multi-tenant management ListOrganizationsResponse organizations = scalekitClient.organizations() .listOrganizations(5, "");
if (!organizations.getOrganizations().isEmpty()) { Organization firstOrg = organizations.getOrganizations().get(0); System.out.println("Organization name: " + firstOrg.getDisplayName()); System.out.println("Organization ID: " + firstOrg.getId()); }} catch (ScalekitException error) { System.err.println("Failed to list organizations: " + error.getMessage()); // Implement appropriate error handling}After successfully listing organizations, you’ll need to retrieve the specific directory to begin syncing user and group data. You can retrieve directories using either the organization and directory IDs, or fetch the primary directory for an organization.
try { // Use case: Get specific directory when organization has multiple directories // Examples: Department-specific provisioning, multi-division companies const { directory } = await scalekit.directory.getDirectory('<organization_id>', '<directory_id>'); console.log(`Directory name: ${directory.name}`);
// Use case: Get primary directory for simple provisioning workflows // Examples: Small organizations, single-directory setups const { directory } = await scalekit.directory.getPrimaryDirectoryByOrganizationId('<organization_id>'); console.log(`Primary directory ID: ${directory.id}`);} catch (error) { console.error('Failed to retrieve directory:', error); // Handle error appropriately for your application}try: # Use case: Access specific directory for targeted user sync operations # Examples: Regional offices, business unit-specific provisioning directory = scalekit_client.directory.get_directory( organization_id='<organization_id>', directory_id='<directory_id>' ) print(f'Directory name: {directory.name}')
# Use case: Get primary directory for streamlined user management # Examples: Standard employee provisioning, main company directory primary_directory = scalekit_client.directory.get_primary_directory_by_organization_id( organization_id='<organization_id>' ) print(f'Primary directory ID: {primary_directory.id}')except Exception as error: print(f'Error retrieving directory: {error}') # Implement appropriate error handling// Use case: Retrieve specific directory for granular access control// Examples: Multi-tenant environments, department-level provisioningdirectory, err := scalekitClient.Directory().GetDirectory(ctx, organizationId, directoryId)if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("failed to get directory: %w", err)}fmt.Printf("Directory name: %s\n", directory.Name)
// Use case: Get primary directory for simplified user management// Examples: Automated provisioning workflows, bulk user importsdirectory, err := scalekitClient.Directory().GetPrimaryDirectoryByOrganizationId(ctx, organizationId)if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("failed to get primary directory: %w", err)}fmt.Printf("Primary directory ID: %s\n", directory.ID)try { // Use case: Access specific directory for detailed user management // Examples: Custom provisioning logic, directory-specific rules Directory directory = scalekitClient.directories() .getDirectory("<directoryId>", "<organizationId>"); System.out.println("Directory name: " + directory.getName());
// Use case: Get primary directory for standard provisioning workflows // Examples: Employee onboarding, automated user sync Directory primaryDirectory = scalekitClient.directories() .getPrimaryDirectoryByOrganizationId("<organizationId>"); System.out.println("Primary directory ID: " + primaryDirectory.getId());} catch (ScalekitException error) { System.err.println("Failed to retrieve directory: " + error.getMessage()); // Implement appropriate error handling}Once you have the directory information, you can fetch users within that directory. This is commonly used for bulk user synchronization and maintaining an up-to-date user database.
try { // Use case: Bulk user synchronization and provisioning // Examples: New customer onboarding, scheduled user data sync const { users } = await scalekit.directory.listDirectoryUsers('<organization_id>', '<directory_id>');
// Process each user for provisioning or updates users.forEach(user => { console.log(`User email: ${user.email}, Name: ${user.name}`); // TODO: Implement your user provisioning logic here });} catch (error) { console.error('Failed to list directory users:', error); // Handle error appropriately for your application}try: # Use case: Automated user provisioning workflows # Examples: HR system integration, bulk user imports directory_users = scalekit_client.directory.list_directory_users( organization_id='<organization_id>', directory_id='<directory_id>' )
# Process each user for local database updates for user in directory_users: print(f'User email: {user.email}, Name: {user.name}') # TODO: Implement your user synchronization logic hereexcept Exception as error: print(f'Error listing directory users: {error}') # Implement appropriate error handling// Configure pagination options for large user directoriesoptions := &ListDirectoryUsersOptions{ PageSize: 50, // Adjust based on your needs PageToken: "",}
// Use case: Paginated user retrieval for large directories// Examples: Enterprise customer provisioning, regular sync jobsdirectoryUsers, err := scalekitClient.Directory().ListDirectoryUsers(ctx, organizationId, directoryId, options)if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("failed to list directory users: %w", err)}
// Process each userfor _, user := range directoryUsers.Users { fmt.Printf("User email: %s, Name: %s\n", user.Email, user.Name) // TODO: Implement your user provisioning logic}// Configure options for user listing with paginationvar options = ListDirectoryResourceOptions.builder() .pageSize(50) // Adjust based on your requirements .pageToken("") .includeDetail(true) // Include detailed user information .build();
try { // Use case: Enterprise user management and synchronization // Examples: Scheduled sync tasks, user provisioning automation ListDirectoryUsersResponse usersResponse = scalekitClient.directories() .listDirectoryUsers(directory.getId(), organizationId, options);
// Process each user for provisioning for (User user : usersResponse.getUsers()) { System.out.println("User email: " + user.getEmail() + ", Name: " + user.getName()); // TODO: Implement your user provisioning logic here }} catch (ScalekitException error) { System.err.println("Failed to list directory users: " + error.getMessage()); // Implement appropriate error handling}Groups are essential for implementing role-based access control (RBAC) in your application. After retrieving users, you can fetch groups to manage permissions and access levels based on organizational structure.
try { // Use case: Role-based access control implementation // Examples: Department-level permissions, project-based access const { groups } = await scalekit.directory.listDirectoryGroups( '<organization_id>', '<directory_id>', );
// Process each group for RBAC setup groups.forEach(group => { console.log(`Group name: ${group.name}, ID: ${group.id}`); // TODO: Implement your group-based permission logic here });} catch (error) { console.error('Failed to list directory groups:', error); // Handle error appropriately for your application}try: # Use case: Department-based access control # Examples: Engineering vs Sales permissions, project team access directory_groups = scalekit_client.directory.list_directory_groups( directory_id='<directory_id>', organization_id='<organization_id>' )
# Process each group for permission mapping for group in directory_groups: print(f'Group name: {group.name}, ID: {group.id}') # TODO: Implement your group-based permission logic hereexcept Exception as error: print(f'Error listing directory groups: {error}') # Implement appropriate error handling// Configure pagination for group listingoptions := &ListDirectoryGroupsOptions{ PageSize: 25, // Adjust based on expected group count PageToken: "",}
// Use case: Organizational role management// Examples: Enterprise role hierarchy, department-based accessdirectoryGroups, err := scalekitClient.Directory().ListDirectoryGroups(ctx, organizationId, directoryId, options)if err != nil { return fmt.Errorf("failed to list directory groups: %w", err)}
// Process each group for RBAC implementationfor _, group := range directoryGroups.Groups { fmt.Printf("Group name: %s, ID: %s\n", group.Name, group.ID) // TODO: Implement your group-based permission logic}// Configure options for detailed group informationvar options = ListDirectoryResourceOptions.builder() .pageSize(25) // Adjust based on your requirements .pageToken("") .includeDetail(true) // Include group membership details .build();
try { // Use case: Enterprise permission management // Examples: Role assignments, access level configurations ListDirectoryGroupsResponse groupsResponse = scalekitClient.directories() .listDirectoryGroups(directory.getId(), organizationId, options);
// Process each group for permission mapping for (Group group : groupsResponse.getGroups()) { System.out.println("Group name: " + group.getName() + ", ID: " + group.getId()); // TODO: Implement your group-based permission logic here }} catch (ScalekitException error) { System.err.println("Failed to list directory groups: " + error.getMessage()); // Implement appropriate error handling}Scalekit’s Directory API provides a simple way to fetch user and group information on-demand. Refer to our API reference to explore more capabilities.
While the Directory API is perfect for scheduled synchronization, webhooks enable immediate, real-time user provisioning. When directory providers send events to Scalekit, we forward them instantly to your application, allowing you to respond to user changes as they happen.
This approach is ideal for scenarios requiring immediate action, such as new employee onboarding or emergency access revocation.
Create a webhook endpoint to receive real-time events from directory providers. After implementing your endpoint, register it in Dashboard > Webhooks where you’ll receive a secret for payload verification.
app.post('/webhook', async (req, res) => { // Security: ALWAYS verify requests are from Scalekit before processing // This prevents unauthorized parties from triggering your provisioning logic
const event = req.body; const headers = req.headers; const secret = process.env.SCALEKIT_WEBHOOK_SECRET;
try { // Verify webhook signature to prevent replay attacks and forged requests await scalekit.verifyWebhookPayload(secret, headers, event); } catch (error) { console.error('Webhook signature verification failed:', error); // Return 400 for invalid signatures - this prevents processing malicious requests return res.status(400).json({ error: 'Invalid signature' }); }
try { // Use case: Real-time user provisioning based on directory events // Examples: New hire onboarding, emergency access revocation, role changes const { email, name } = event.data;
// Process the webhook event based on its type switch (event.type) { case 'organization.directory.user_created': await createUserAccount(email, name); break; case 'organization.directory.user_updated': await updateUserAccount(email, name); break; case 'organization.directory.user_deleted': await deactivateUserAccount(email); break; default: console.log(`Unhandled event type: ${event.type}`); }
res.status(201).json({ message: 'Webhook processed successfully' }); } catch (processingError) { console.error('Failed to process webhook event:', processingError); res.status(500).json({ error: 'Processing failed' }); }});from fastapi import FastAPI, Request, HTTPExceptionimport osimport json
app = FastAPI()
@app.post("/webhook")async def api_webhook(request: Request): # Security: ALWAYS verify webhook signatures before processing events # This prevents unauthorized webhook calls and replay attacks
headers = request.headers body = await request.json()
try: # Verify webhook payload using the secret from Scalekit dashboard # Get this from Dashboard > Webhooks after registering your endpoint is_valid = scalekit_client.verify_webhook_payload( secret=os.getenv("SCALEKIT_WEBHOOK_SECRET"), headers=headers, payload=json.dumps(body).encode('utf-8') )
if not is_valid: raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Invalid webhook signature")
except Exception as verification_error: print(f"Webhook verification failed: {verification_error}") raise HTTPException(status_code=400, detail="Webhook verification failed")
# Use case: Instant user provisioning based on directory events # Examples: Automated onboarding, immediate access revocation, role updates try: event_type = body.get("type") event_data = body.get("data", {}) email = event_data.get("email") name = event_data.get("name")
if event_type == "organization.directory.user_created": await create_user_account(email, name) elif event_type == "organization.directory.user_updated": await update_user_account(email, name) elif event_type == "organization.directory.user_deleted": await deactivate_user_account(email)
return JSONResponse(status_code=201, content={"status": "processed"})
except Exception as processing_error: print(f"Failed to process webhook: {processing_error}") raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Event processing failed")@PostMapping("/webhook")public ResponseEntity<String> webhook( @RequestBody String body, @RequestHeader Map<String, String> headers) {
// Security: ALWAYS verify webhook signatures before processing // This prevents malicious webhook calls and protects against replay attacks
String secret = System.getenv("SCALEKIT_WEBHOOK_SECRET");
try { // Verify webhook signature using Scalekit SDK boolean isValid = scalekitClient.webhook() .verifyWebhookPayload(secret, headers, body.getBytes());
if (!isValid) { return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("Invalid webhook signature"); }
} catch (Exception verificationError) { System.err.println("Webhook verification failed: " + verificationError.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("Webhook verification failed"); }
try { // Use case: Real-time user lifecycle management // Examples: Employee onboarding, access termination, role modifications ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); JsonNode rootNode = mapper.readTree(body);
String eventType = rootNode.get("type").asText(); JsonNode data = rootNode.get("data");
switch (eventType) { case "organization.directory.user_created": String email = data.get("email").asText(); String name = data.get("name").asText(); createUserAccount(email, name); break; case "organization.directory.user_updated": updateUserAccount(data); break; case "organization.directory.user_deleted": deactivateUserAccount(data.get("email").asText()); break; default: System.out.println("Unhandled event type: " + eventType); }
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.CREATED).body("Webhook processed");
} catch (Exception processingError) { System.err.println("Failed to process webhook event: " + processingError.getMessage()); return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR) .body("Event processing failed"); }}// Security: Store webhook secret securely in environment variables// Get this from Dashboard > Webhooks after registering your endpointwebhookSecret := os.Getenv("SCALEKIT_WEBHOOK_SECRET")
http.HandleFunc("/webhook", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) { // Security: ALWAYS verify webhook signatures before processing events // This prevents unauthorized webhook calls and replay attacks
if r.Method != http.MethodPost { http.Error(w, "Method not allowed", http.StatusMethodNotAllowed) return }
body, err := io.ReadAll(r.Body) if err != nil { http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusBadRequest) return } defer r.Body.Close()
// Extract webhook headers for verification headers := map[string]string{ "webhook-id": r.Header.Get("webhook-id"), "webhook-signature": r.Header.Get("webhook-signature"), "webhook-timestamp": r.Header.Get("webhook-timestamp"), }
// Verify webhook signature to prevent malicious requests _, err = scalekitClient.VerifyWebhookPayload(webhookSecret, headers, body) if err != nil { http.Error(w, "Invalid webhook signature", http.StatusBadRequest) return }
// Use case: Instant user provisioning and lifecycle management // Examples: Real-time onboarding, emergency access revocation, role synchronization var webhookEvent WebhookEvent if err := json.Unmarshal(body, &webhookEvent); err != nil { http.Error(w, "Invalid webhook payload", http.StatusBadRequest) return }
switch webhookEvent.Type { case "organization.directory.user_created": err = createUserAccount(webhookEvent.Data.Email, webhookEvent.Data.Name) case "organization.directory.user_updated": err = updateUserAccount(webhookEvent.Data) case "organization.directory.user_deleted": err = deactivateUserAccount(webhookEvent.Data.Email) default: fmt.Printf("Unhandled event type: %s\n", webhookEvent.Type) }
if err != nil { http.Error(w, "Failed to process webhook", http.StatusInternalServerError) return }
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusCreated) w.Write([]byte(`{"status": "processed"}`))})After implementing your secure webhook endpoint, register it in the Scalekit dashboard to start receiving events:
https://your-app.com/api/webhooks/scalekit)organization.directory.user_created - New user provisioningorganization.directory.user_updated - User profile changesorganization.directory.user_deleted - User deactivationorganization.directory.group_created - New group creationorganization.directory.group_updated - Group modificationsOnce registered, your webhook endpoint will start receiving event payloads from directory providers in real-time.
Scalekit standardizes event payloads across different directory providers, ensuring consistent data structure regardless of whether your customers use Azure AD, Okta, Google Workspace, or other providers.
When directory changes occur, Scalekit sends events with the following structure:
{ "id": "evt_1234567890", "type": "organization.directory.user_created", "data": { "email": "john.doe@company.com", "name": "John Doe", "organization_id": "org_12345", "directory_id": "dir_67890" }, "timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"}You have now successfully implemented and registered a webhook endpoint, enabling your application to receive real-time events for automated user provisioning. Your system can now respond instantly to directory changes, providing seamless user lifecycle management.
Refer to our webhook events documentation for the complete list of available event types and payload structures.